R語言非線性最小二乘
模擬回歸分析現實世界的數據我們這是很少觀察到,該模型的方程是線性方程給出的線性曲線圖的情況。大多數時候真實世界數據模型的方程涉及更高程度就像3的指數或一個正弦函數數學函數。 在這樣的情況下,該模型的曲線圖給出了一個曲線而不是一條線。線性和非線性回歸的目的是為了調整模型的參數的值,以發現最接近的數據的直線或曲線。在尋找這些值,我們將能夠以良好的精度來估計響應變量。
在最小二乘回歸我們建立在從回歸曲線的不同點的垂直距離的平方及被最小化的回歸模型。我們通常開始與定義的模型和假設為係數的一些值。然後,我們應用R的nls() 函數,以獲得更準確的值隨著可信區間。
語法
創建一個非線性最小二乘測試,在R語言中的基本語法是:
nls(formula, data, start)
以下是所使用的參數的說明:
- formula 是一種非線性模型公式包括變量和參數。
- data 是用於評估/計算公式中變量的數據幀。
- start 是命名列表或起始命名估算的數字向量。
示例
我們會考慮其係數假設非線性模型的初始值。下一步,我們將看到的是,這些假設值的可信區間,這樣我們就可以判斷這些值如何在模型中。
所以,讓我們來看看下麵的公式用於此目的:
a = b1*x^2+b2
讓我們假定初始係數為1和3,以及適合將這些值到 nls()函數。
xvalues <- c(1.6,2.1,2,2.23,3.71,3.25,3.4,3.86,1.19,2.21) yvalues <- c(5.19,7.43,6.94,8.11,18.75,14.88,16.06,19.12,3.21,7.58) # Give the chart file a name. png(file = "nls.png") # Plot these values. plot(xvalues,yvalues) # Take the assumed values and fit into the model. model <- nls(yvalues ~ b1*xvalues^2+b2,start = list(b1=1,b2=3)) # Plot the chart with new data by fitting it to a prediction from 100 data points. new.data <- data.frame(xvalues = seq(min(xvalues),max(xvalues),len=100)) lines(new.data$xvalues,predict(model,newdata=new.data)) # Save the file. dev.off() # Get the sum of the squared residuals. print(sum(resid(model)^2)) # Get the confidence intervals on the chosen values of the coefficients. print(confint(model))
當我們上麵的代碼執行時,它產生以下結果:
[1] 1.081935
Waiting for profiling to be done...
2.5% 97.5%
b1 1.137708 1.253135
b2 1.497364 2.496484
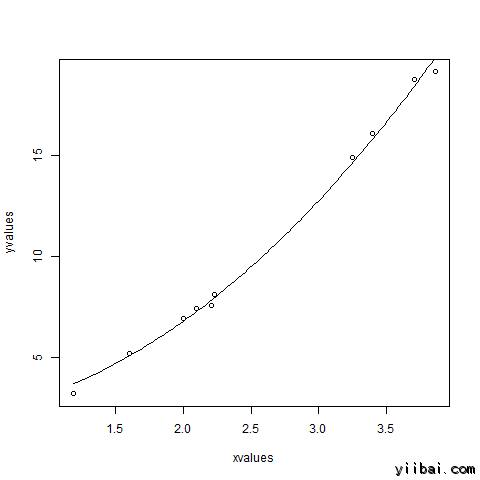
我們可以得出結論,當 b2 的值更接近 2 而不是 3 時,b1 的值更接近 1。


