Java多線程
Java提供了對多線程編程的內置支持。多線程程序中包含可以同時運行兩個或多個部分。這樣一個程序的每個部分稱為一個線程,每個線程定義一個單獨的執行路徑。
多線程是多任務的一種特殊形式。多線程需要比多任務處理開銷更少。
需要定義其他術語相關:線程和進程。進程包括操作係統,它可以包含一個或多個線程分配的內存空間。線程不能單獨存在,它必須是一個進程的一部分。一個進程仍然在運行,直到所有的非守護線程都執行完畢。
多線程能夠編寫非常高效的程序,最大限度地利用CPU,因為空閒時間可以保持在最低限度。
線程的生命周期:
一個線程經曆在其生命周期的不同階段。例如,一個線程產生,開始,運行,然後死亡。下圖顯示了一個線程的整個生命周期。
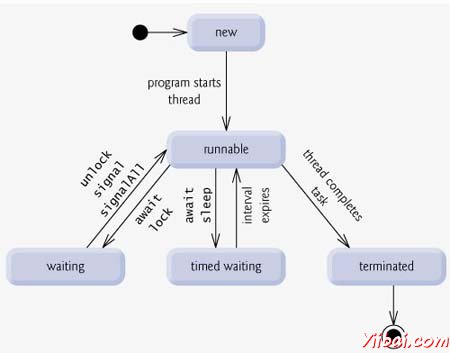
上述階段進行了說明:
-
New: 一個新的線程開始在新的狀態的生命周期。它仍然在此狀態,直到程序啟動的線程。它也被稱為出生線程。
-
Runnable: 經過一個新生的線程啟動時,該線程進入可運行狀態。處於這種狀態的線程將被視為執行其任務。
-
Waiting: 有時候,一個線程轉換到等待狀態,而線程等待另一個線程來執行任務。一個線程轉換回可運行狀態,隻有當另一個線程發出信號的等待線程繼續執行。
-
Timed waiting: 可運行的線程可以輸入指定的時間間隔定時等待狀態。處於這種狀態的線程轉換回可運行狀態時的時間間隔期滿時或在等待事件發生。
-
Terminated: 可運行的線程進入終止狀態,當它完成了自己的任務,否則終止。
線程的優先級:
每一個Java線程都有一個優先級,可以幫助操作係統決定哪個線程預定的順序。
Java優先級是在MIN_PRIORITY(常數1)和MAX_PRIORITY(常數10)之間的範圍內。默認情況下,每個線程優先NORM_PRIORITY(常數5)。
線程具有更高的優先級是比較重要的一個程序和低優先級的線程之前應該分配處理器時間。但是,線程優先級不能保證哪個線程的執行順序和非常依賴平台。
創建線程:
Java定義在此可以完成兩種方式:
-
可以實現Runnable接口。
-
可以擴展Thread類本身。
通過實現Runnable創建線程:
創建一個線程,最簡單的方法是創建一個實現Runnable接口的類。
為了實現Runnable,這個類需要實現隻有一個單一的方法 run(),它是這樣聲明的:
public void run( )
定義構成新線程 run()方法的代碼內部。重要的是要明白的run()可以調用其他方法,使用其他類,並聲明變量,就像主線程可以是很重要的。
當創建一個實現Runnable類,會從類中實例化線程的對象。線程定義了多個構造函數。我們將使用一個如下所示:
Thread(Runnable threadOb, String threadName);
在這裡,threadOb是實現Runnable接口和新線程的名稱是由threadName指定一個類的實例。
創建新線程後,它不會啟動運行,直到調用它的start()方法,它是內線程聲明。start()方法如下所示:
void start( );
例子:
下麵是創建一個新的線程並開始運行一個例子:
// Create a new thread. class NewThread implements Runnable { Thread t; NewThread() { // Create a new, second thread t = new Thread(this, "Demo Thread"); System.out.println("Child thread: " + t); t.start(); // Start the thread } // This is the entry point for the second thread. public void run() { try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); // Let the thread sleep for a while. Thread.sleep(50); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child interrupted."); } System.out.println("Exiting child thread."); } } public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String args[]) { new NewThread(); // create a new thread try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Main Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(100); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Main thread interrupted."); } System.out.println("Main thread exiting."); } }
這將產生以下結果:
Child thread: Thread[Demo Thread,5,main] Main Thread: 5 Child Thread: 5 Child Thread: 4 Main Thread: 4 Child Thread: 3 Child Thread: 2 Main Thread: 3 Child Thread: 1 Exiting child thread. Main Thread: 2 Main Thread: 1 Main thread exiting.
通過擴展Thread創建線程:
創建一個線程的第二種方式是創建可擴展條條一個新的類,然後創建一個類的實例。
擴展類必須重寫run()方法,這是切入點的新線程。它還必須調用start()開始執行新線程。
例子:
下麵是重寫擴展線程前麵的程序:
// Create a second thread by extending Thread class NewThread extends Thread { NewThread() { // Create a new, second thread super("Demo Thread"); System.out.println("Child thread: " + this); start(); // Start the thread } // This is the entry point for the second thread. public void run() { try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Child Thread: " + i); // Let the thread sleep for a while. Thread.sleep(50); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Child interrupted."); } System.out.println("Exiting child thread."); } } public class ExtendThread { public static void main(String args[]) { new NewThread(); // create a new thread try { for(int i = 5; i > 0; i--) { System.out.println("Main Thread: " + i); Thread.sleep(100); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Main thread interrupted."); } System.out.println("Main thread exiting."); } }
這將產生以下結果:
Child thread: Thread[Demo Thread,5,main] Main Thread: 5 Child Thread: 5 Child Thread: 4 Main Thread: 4 Child Thread: 3 Child Thread: 2 Main Thread: 3 Child Thread: 1 Exiting child thread. Main Thread: 2 Main Thread: 1 Main thread exiting.
線程方法:
以下是在Thread類提供重要的方法列表。
| SN | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
public void start() Starts the thread in a separate path of execution, then invokes the run() method on this Thread object. |
| 2 |
public void run() If this Thread object was instantiated using a separate Runnable target, the run() method is invoked on that Runnable object. |
| 3 |
public final void setName(String name) Changes the name of the Thread object. There is also a getName() method for retrieving the name. |
| 4 |
public final void setPriority(int priority) Sets the priority of this Thread object. The possible values are between 1 and 10. |
| 5 |
public final void setDaemon(boolean on) A parameter of true denotes this Thread as a daemon thread. |
| 6 |
public final void join(long millisec) The current thread invokes this method on a second thread, causing the current thread to block until the second thread terminates or the specified number of milliseconds passes. |
| 7 |
public void interrupt() Interrupts this thread, causing it to continue execution if it was blocked for any reason. |
| 8 |
public final boolean isAlive() Returns true if the thread is alive, which is any time after the thread has been started but before it runs to completion. |
以前的方法是在一個特定的Thread對象調用。在Thread類下麵的方法都是靜態的。調用靜態方法之一執行當前正在運行的線程上運行。
| SN | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
public static void yield() Causes the currently running thread to yield to any other threads of the same priority that are waiting to be scheduled. |
| 2 |
public static void sleep(long millisec) Causes the currently running thread to block for at least the specified number of milliseconds. |
| 3 |
public static boolean holdsLock(Object x) Returns true if the current thread holds the lock on the given Object. |
| 4 |
public static Thread currentThread() Returns a reference to the currently running thread, which is the thread that invokes this method. |
| 5 |
public static void dumpStack() Prints the stack trace for the currently running thread, which is useful when debugging a multithreaded application. |
例子:
下麵ThreadClassDemo程序演示了一些Thread類的這些方法。考慮類DisplayMessage它實現了Runnable:
// File Name : DisplayMessage.java // Create a thread to implement Runnable public class DisplayMessage implements Runnable { private String message; public DisplayMessage(String message) { this.message = message; } public void run() { while(true) { System.out.println(message); } } }
下麵是另一個類,它擴展了Thread類:
// File Name : GuessANumber.java // Create a thread to extentd Thread -by www.gitbook.net public class GuessANumber extends Thread { private int number; public GuessANumber(int number) { this.number = number; } public void run() { int counter = 0; int guess = 0; do { guess = (int) (Math.random() * 100 + 1); System.out.println(this.getName() + " guesses " + guess); counter++; }while(guess != number); System.out.println("** Correct! " + this.getName() + " in " + counter + " guesses.**"); } }
以下是主要的程序,利用了上述定義的類:
// File Name : ThreadClassDemo.java public class ThreadClassDemo { public static void main(String [] args) { Runnable hello = new DisplayMessage("Hello"); Thread thread1 = new Thread(hello); thread1.setDaemon(true); thread1.setName("hello"); System.out.println("Starting hello thread..."); thread1.start(); Runnable bye = new DisplayMessage("Goodbye"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(bye); thread2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); thread2.setDaemon(true); System.out.println("Starting goodbye thread..."); thread2.start(); System.out.println("Starting thread3..."); Thread thread3 = new GuessANumber(27); thread3.start(); try { thread3.join(); }catch(InterruptedException e) { System.out.println("Thread interrupted."); } System.out.println("Starting thread4..."); Thread thread4 = new GuessANumber(75); thread4.start(); System.out.println("main() is ending..."); } }
這將產生以下結果。可以試試這個例子多次,每次都會得到不同的結果。
Starting hello thread... Starting goodbye thread... Hello Hello Hello Hello Hello Hello Goodbye Goodbye Goodbye Goodbye Goodbye .......
主要線程概念:
多線程編程,需要具備以下概念非常必要:
使用多線程:
有效地利用多線程支持的關鍵是同時,而非串行。例如,當有一個程序,可以並發執行中兩個子係統,使它們各個線程運行。
隻要仔細地使用多線程,可以創建非常高效的程序。要注意的是:如果你創建了太多的線程,可以實際降低程序的性能,而不是提高它。
請記住,一些開銷與上下文切換有關。如果創建了太多的線程,更多的CPU時間會花在不斷變化的環境不是執行程序!


